Webhooks
Set up webhooks in your Dashboard to receive updates in real-time regarding your orders, products, and employees. Learn how to create endpoints and view available events to stay up to date with your GroWrk activity.
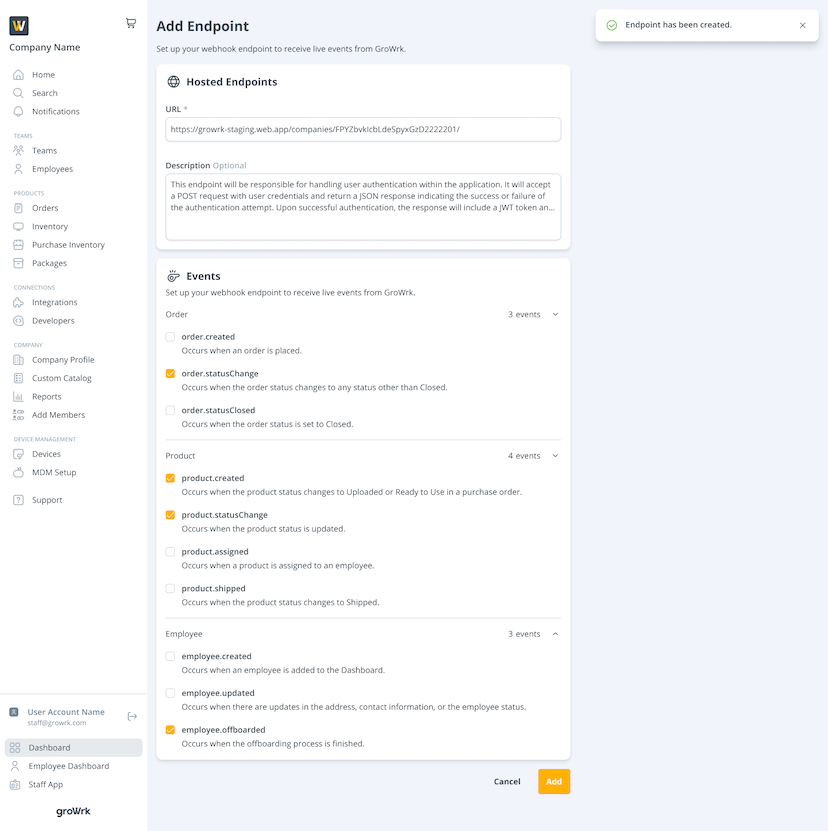
- In the Developers page, select the Webhooks tab.
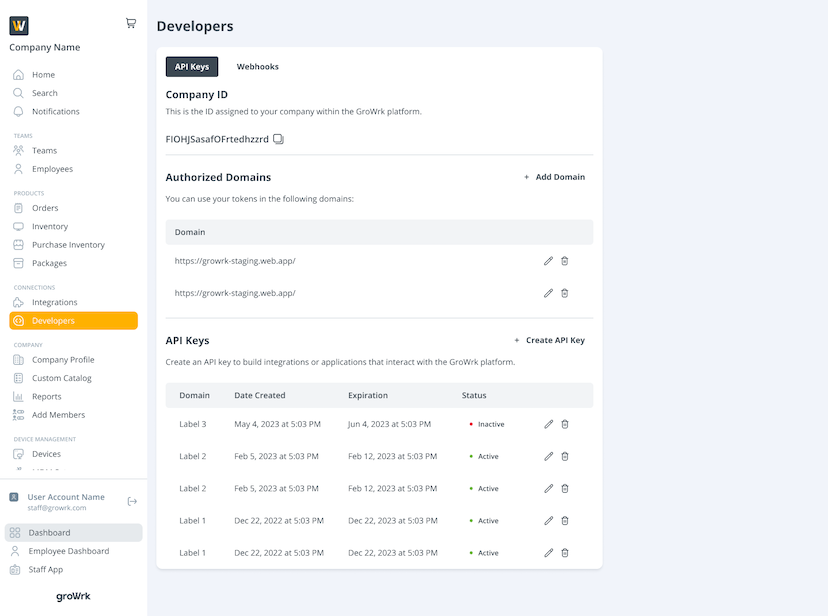
- Select Add Endpoint in the Hosted Endpoints section.
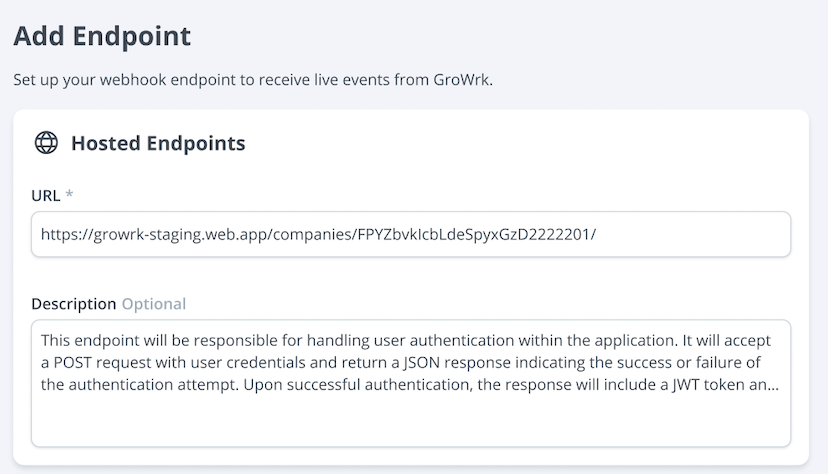
- Enter the URL and optional description.
- Select events based on orders, products, or employees. You must select at least one event to continue.
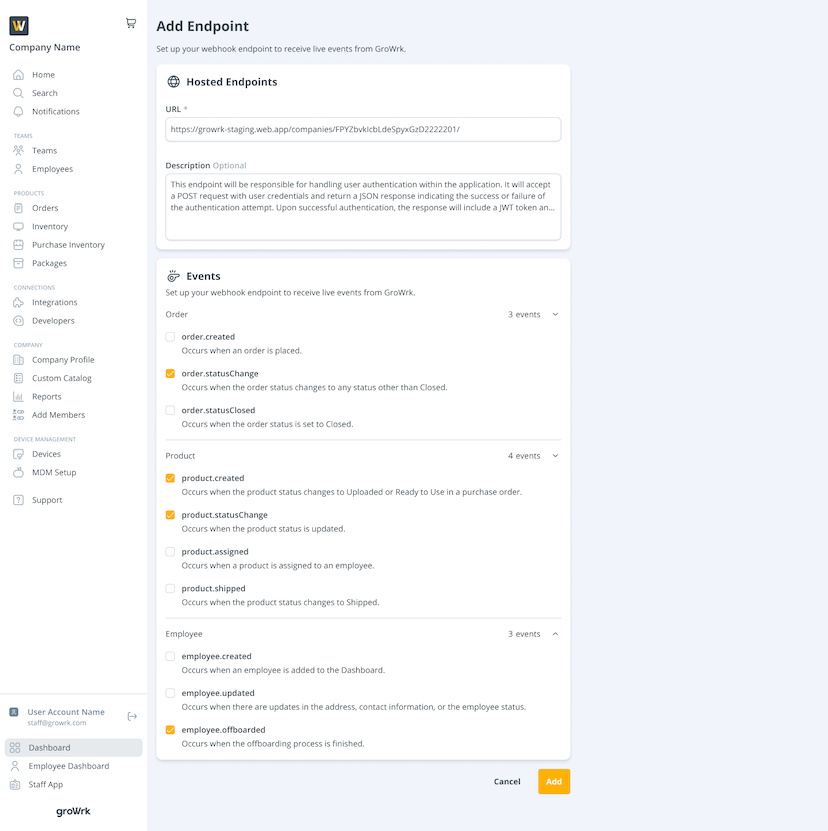
- Select Add. You’ll be notified that the endpoint has been created.
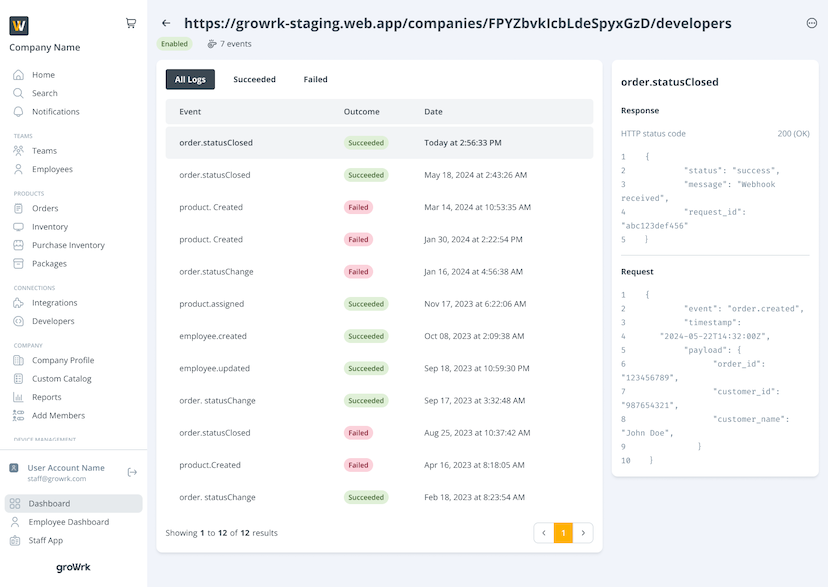
Endpoints page
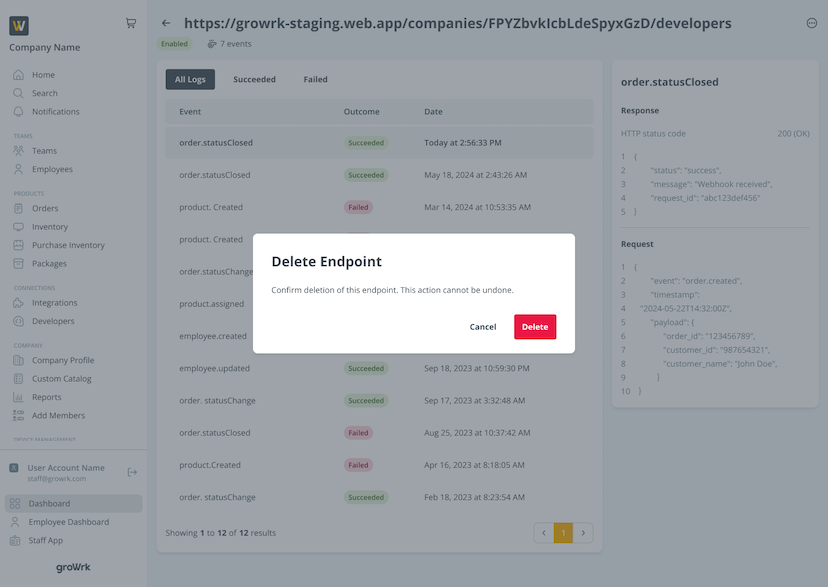
The Endpoints page lists all logs starting from the most recent. You can view by succeeded and failed attempts by selecting the respective tabs.
On the top right corner, there is a menu to edit, enable/disable, or delete the endpoint.
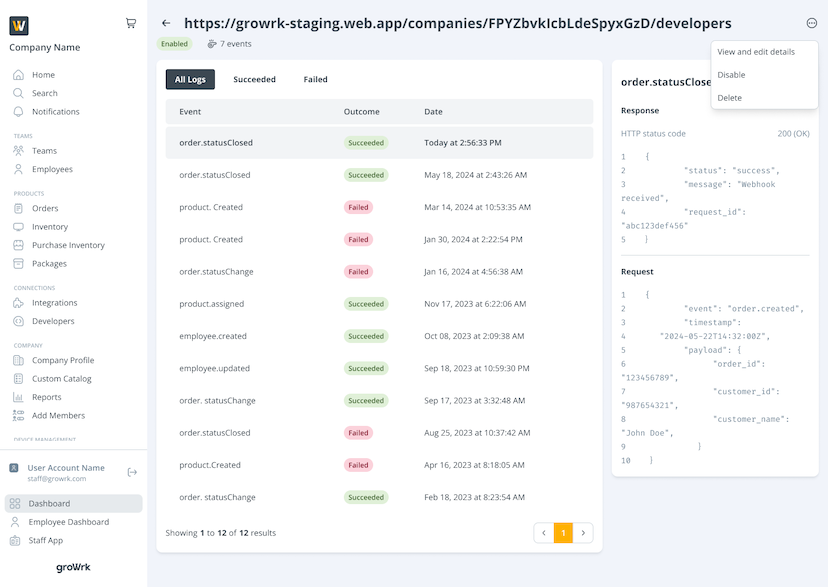
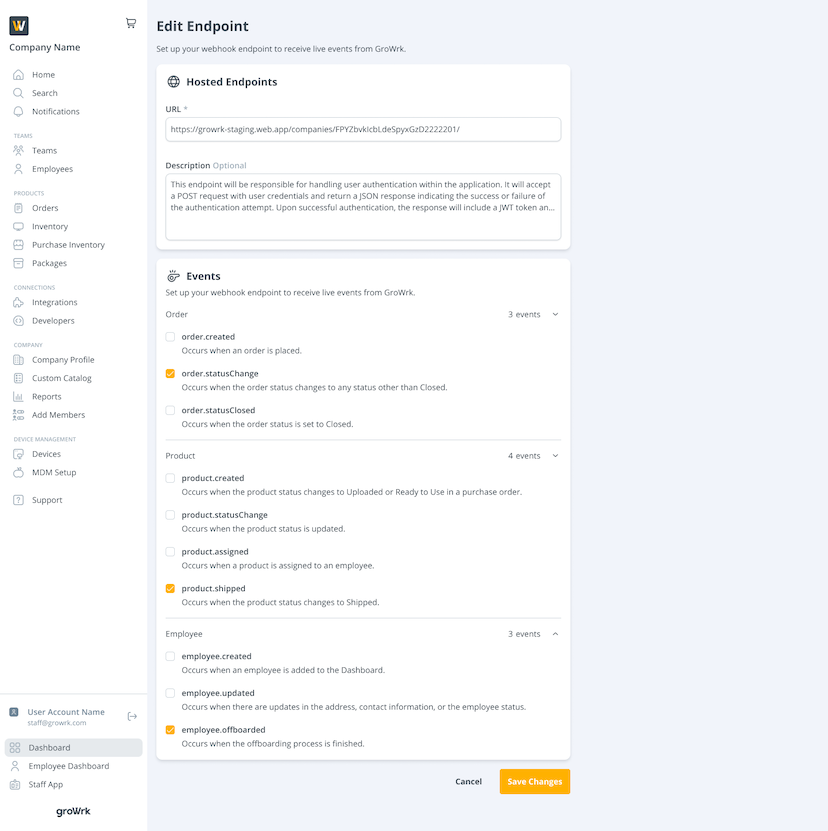
By selecting View and edit details, you will be taken to the same page as the Add Endpoint page to edit the details.
The Disable button is visible only when the endpoint is enabled, and the Enable button appears when the endpoint is disabled.
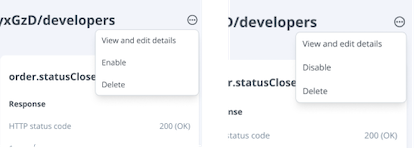
By selecting Delete, the endpoint will no longer be in use.
Events
Here are the events you can subscribe to:
order.created: Triggered when a new order is placed.
order.statusChange: Triggered when the order status is updated.
order.statusClosed: Triggered when an order is closed.
product.created: Triggered when a new product is added.
product.statusChange: Triggered when the product status is updated.
product.assigned: Triggered when the product is assigned to an employee.
product.shipped: Triggered when the product status changes to Shipped.
employee.created: Triggered when an employee is added to the Dashboard.
employee.updated: Triggered when an employee is updated.
employee.offboarded: Triggered when the offboarding process is finished.
Payloads
Each webhook event sends a JSON payload containing relevant data. Each payload will contain the following fields:
- Event
- Timestamp
- Company ID
Example payload:
{
"event": "order.created",
"timestamp": "2024-08-17T12:34:56Z",
"companyId": "123",
"orders": [{
"id": "12345",
"url": "https://app.growrk.com/companies/123/order/12345",
"createdAt": "2024-08-16T10:45:32Z",
"status": "order placed",
"closedAt": null,
"regionId": "us",
"country": "US",
"type": "Purchase for Inventory",
"cost": 1102.5,
"employee": {
"id": "emp-12345",
"displayName": "John Doe",
"email": "johndoe@example.com",
"path": "https://app.growrk.com/companies/123/employees/emp-12345",
},
"shippingAddress": "1234 Elm St, Springfield, US",
"collectionAddress": null,
"contactAttempt": 1, // Optional
"poNumber": "PO987654", // Optional
"expediteShipping": true // Optional
}]
}
Payload fields for order events
- Orders
- ID
- URL
- Created at
- Status
- Closed at
- Region ID
- Country
- Type
- Cost
- Employee
- ID
- Display name
- Path
- Shipping address
- Collection address
- Contact attempt
- PO number
- Expedited shipping
Payload fields for product events
- Products
- ID
- URL
- Created at
- Status
- Assigned
- Employee
- Managed by
- Manufacturer
- Model
- Region ID
- Serial number
- Title
- Specs
- RAM
- Storage
- CPU
- MDM
- Condition
- Order ID
- Arrival date
- Wiped
- Custom notes
- Charger
- Location
- PO
- PIN
- Legal hold status
Payload fields for employee events
- Employees
- ID
- URL
- Created at
- Status
- Secondary email
- Display name
- Country
- Team ID
- Dashboard
- Temporary address
- Tax ID
- Start date
- T-shirt size
- Annual compensation
- Date of birth
- Department
- Division
- Job title
- Manager
- Nationality
- Pay rate
- Pay frequency
- Employment type
- National ID
- Gender
- Pronouns
- Marital status
- Profile picture
- Emergency contact
- Name
- Phone
Verifying signatures
To ensure the webhook payloads are coming from GroWrk, a signature is included in the request headers. Here is an example header:
x-growrk-signature: KQN-i8I5CUgMo5vYcn...
To validate a signature:
- Get the
x-growrk-signatureheader from the request. - Use HMAC SHA-256 to hash the request body using your webhook secret to recreate the signature.
- If the recreated signature matches the one in the header, the payload is authentic.
Here’s an example in Node.js:
const crypto = require('crypto');
function validateSignature(requestBody, headerSignature, secret) {
const hash = crypto.createHmac('sha256', secret)
.update(requestBody)
.digest('base64')
.replace(/\+/g, '-').replace(/\//g, '_');
return hash === headerSignature;
}